

Blood viscosity is a major issue: blood that is too viscous can form dangerous internal clots, while blood that is too thin will not clot this can lead to dangerous blood loss and even death. Viscosity can be of critical importance in medicine as fluids are introduced into the body intravenously.

Lubricants that are too thin provide too little protection for moving parts. Lubricants that are too viscous can jam and clog pipelines. Manufacturing equipment requires appropriate lubrication to run smoothly. Some viscous fluids add texture to foods honey, for example, is quite viscous and can change the "mouth feel" of a dish. A thick potato and leek soup, for example, when it is less viscous, becomes French vichyssoise. Different cuisines also rely on the viscosity of sauces, soups, and stews. Fats, which are moderately viscous when heated, become solid when chilled. Cooking oils may or may not change viscosity as they heat, while many become much more viscous as they cool. Viscosity plays a significant role in the preparation and serving of food. Some oils have a more stable viscosity, while others react to heat or cold if your oil's viscosity index is low, it may become thinner as it heats, which can cause problems as you operate your car on a hot summer's day. In addition, viscosity also affects the rate of oil consumption and the ease with which your vehicle will start in hot or cold conditions. The high viscosity index lubricants were then improved to reduce start-up friction as well. That's because viscosity affects friction, and friction, in turn, affects heat. Title page figure: Inside the large journal bearing on. When you put oil into your car or truck, you should be aware of its viscosity. To a certain extent, the viscosity index is also an indication of the quality of an oil and serves the comparability of different oil types. The viscosity behaviour at 40 ☌ and 100 ☌ is measured. It refers to the kinematic viscosity of an oil. Step 1 : Consider a ball of radius 2 m and velocity 0.07 m/s with density 7 g/mL is dropped into a liquid with density 1.8 g/ml. The viscosity index (VI) is the behaviour of the lubricant as a function of temperature.
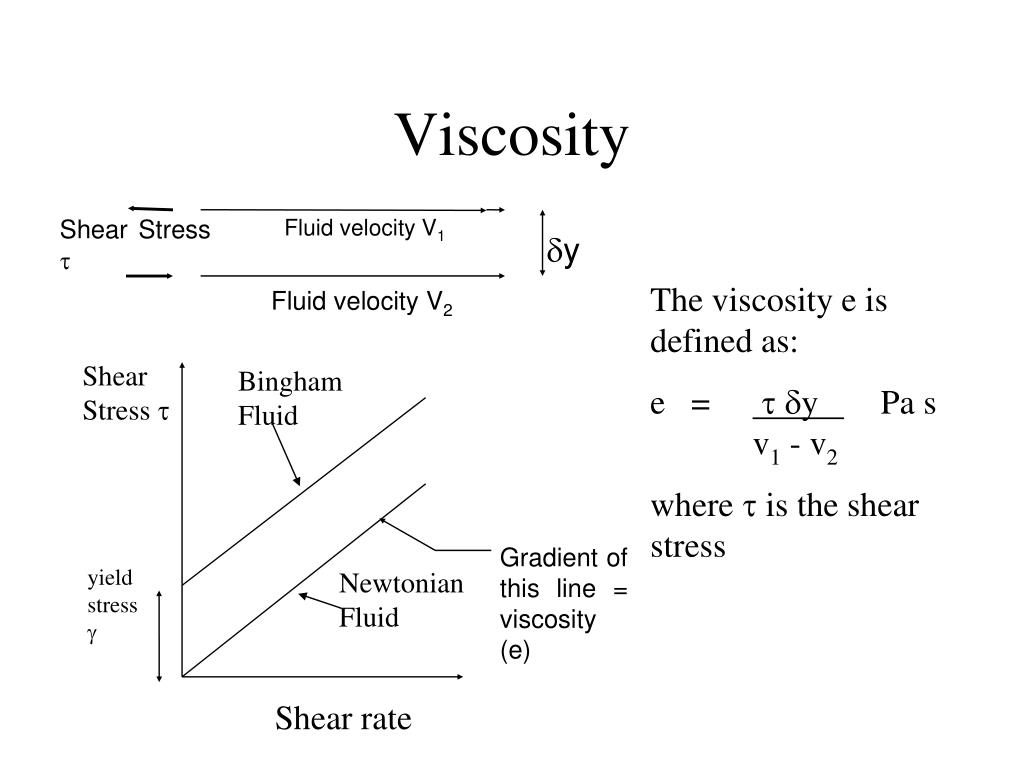
G - Acceleration due to gravity (constant) This tutorial helps you to learn how to calculate viscosity of any liquids/fluids. The common equation used to calculate the viscosity by interpolation between two reference points is with the Ubbelohde. The physical principle of measurement is based on the rate at which a fluid flows under gravity through a capillary tube. The material used should be less than or equal to half of the diameter of the cylinder and should sink in the fluid. The viscosity of Newtonian fluids can be most precisely determined using capillary viscometers. Viscosity can be measured using various methods, where the most common is dropping a material like ball or marble in the liquid container. It can be represented with unit Pascal seconds (Pas). The resistance of a fluid or liquid to flow is termed as the viscosity. How to Calculate Viscosity of Liquids, Fluids? Viscosity of Liquids/Fluids Calculation


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
